10 Common Acids and Chemical Structures
Chemistry One Staab 201617 Acids and Bases Unit 7
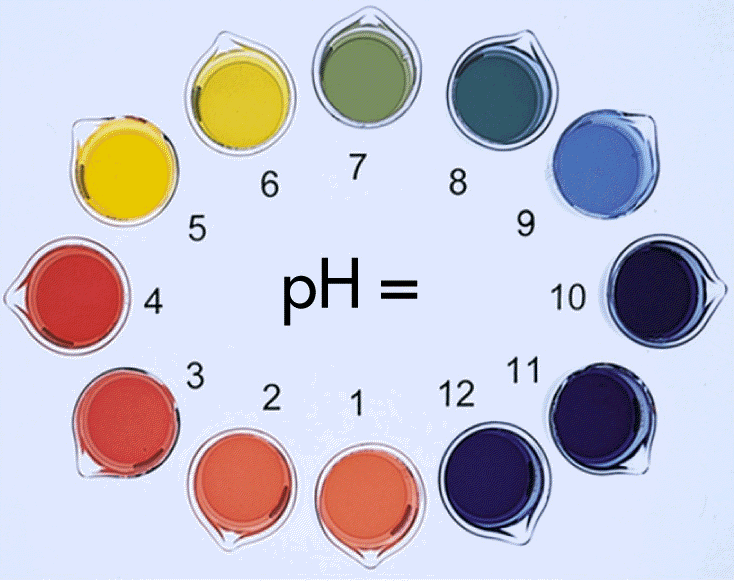
The pH is defined as: pH = -log [H+] where [H +] is the concentration of hydrogen ions in mol dm -3. Similarly, the concentration of H+ of a solution can be calculated if the pH is known by rearranging the above equation to: [H+] = 10-pH. The pH scale is a logarithmic scale with base 10. This means that each value is 10 times the value below.
Acids & Bases (AQA A Level Chemistry) Teaching Resources

Summary of Acids, Bases and Buffers. -Brønsted-Lowry acids are proton donors and bases are proton acceptors. -In water, an acid can donate a proton to form aqueous H + and the conjugate base; a base can accept a proton from water to form OH - and the conjugate acid. -A buffer solution makes able to add a strong acid or base to a solution.
Acids And Bases Online Read Ebook Reader Definition

Conjugate acid-base pairs are a pair of reactants and products that are linked to each other by the transfer of a proton. For example, in the equilibrium reaction below, the ethanoic acid (CH 3 COOH) partially dissociates in solution to form ethanoate (CH 3 COO -) and hydrogen (H +) ions. When equilibrium is established there are CH 3 COOH, H 2.
SOLUTION Chemistry Acids and Bases Studypool

Arrhenius Definition. "an acidic substance is one whose molecular unit contains at least one hydrogen atom that can dissociate, or ionize, when dissolved in water, producing a hydrated hydrogen ion and an anion." hydrochloric acid. HCl → H +(aq) + Cl -(aq) sulfuric acid. H 2 SO 4 → H +(aq) + HSO 4-(aq)
Difference Between Acids and Bases Chemistry Theory Study UPSC, IAS, IPS, SSC CGL, Bank, RRB

Calculating the pH of acidic buffers. 1) A buffer solution was made by adding 2.05 g of sodium ethanoate to 0.500 dm3 of 0.01 mol dm-3 ethanoic acid. Calculate the pH of this solution (Ka for ethanoic acid = 1.74 x 10-5 mol dm-3). Mr CH3COONa = 82.0 mol CH3COONa = 2.05 / 82.0 = 0.0250 mol CH3COO- = 0.0250.
Class 10 Chemistry Worksheet on Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts Set 1

A Brønsted-Lowry acid is a proton donor. A Brønsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor. pH is a measure of the strength of acid. pH = -log 10 [H +] [H +] is concentration of H + in units of mol dm-3.. For a strong acid, total ionisation means that it is easy to tell [H +]..it is simply the same as the acid concentration you are given.. The only exception to that is if the strong acid happens.
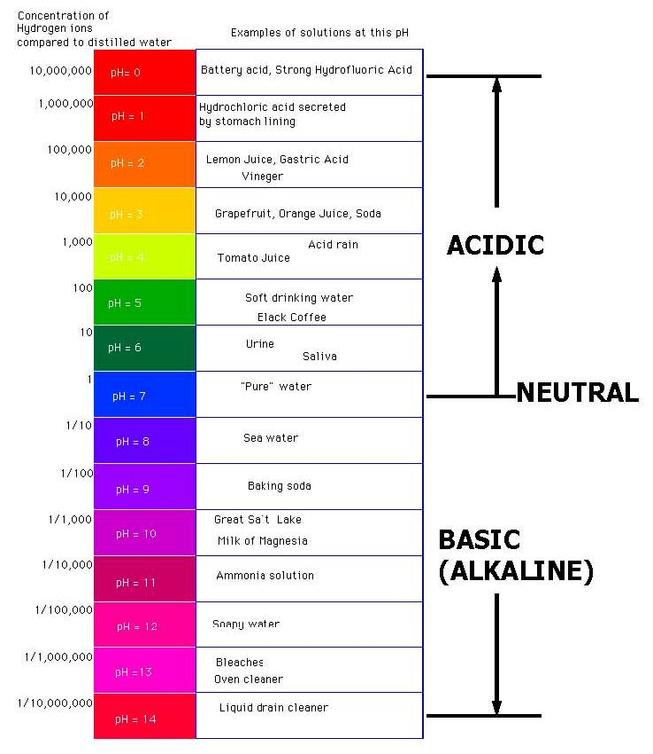
Compound Interest Acids, Alkalis, and the pH Scale

A base is a substance that accepts hydrogen ions or a compound that contains oxide or hydroxide ions. For example, when the base ammonia is added to water, the ammonium ion and hydroxide ions are formed: NH3 (g) + H2O (l) → NH4+ (aq) + OH- (aq) For example, when sodium hydroxide is dissolved in solution, sodium ions and hydroxide ions are.
O Level Chemistry Questions Acids, Bases & Salts O Level Chemistry & IP Chemistry Notes by 10

Complete revision for AQA A Level Chemistry. To buy the PowerPoint used in this video please visit my tes shop - https://www.tes.com/teaching-resources/shop/.
Classroom Chemistry Lesson 9 Acids & Bases MindFuel STEM Store

3.1.12 Acids and bases (A-level only) Acids and bases are important in domestic, environmental and industrial contexts. Acidity in aqueous solutions is caused by hydrogen ions and a logarithmic scale, pH, has been devised to measure acidity. Buffer solutions, which can be made from partially neutralised weak acids, resist changes in pH and find.
High School Chemistry Acids and Bases
A Brønsted base is a species that can accept a proton. For example, a hydroxide (OH -) ion is a Brønsted base as it can accept a proton to form water. OH- (aq) + H+ (aq) → H2O (l) Weak acids dissociating. In an equilibrium reaction, the products are formed at the same rate as the reactants are used. This means that at equilibrium, both.
ACIDS AND BASES

Arrhenius's Definition of Acids and Bases. The earliest definition of acids and bases is Arrhenius's definition which states that: An acid is a substance that forms hydrogen ions H + when dissolved in water, and; A base is a substance that forms hydroxide ions OH-when dissolved in water.; For example, hydrochloric acid (\(\ce{HCl}\)) is an acid because it forms \(\ce{H^{+}}\) when it dissolves.
Properties of Acids and Bases List What is pH?

Acids are usually compounds that contain hydrogen bonded to electronegative element with polar covalent bond, and bases usually have lone pair of electrons. Example of an acid-base reaction: Polar HCl is acting as a proton donor, and the molecule of water, due to the two lone pairs of electrons in the oxygen, is acting as proton acceptor. When.
Chemistry 12.1 What are Acids and Bases? (Part 1 of 2) YouTube

Conjugate acid-base pairs. Relationship between Ka and Kb. Relationship between Ka and Kb. Ka and acid strength. Weak acid equilibrium. Weak base equilibrium. Acid-base properties of salts. pH of salt solutions. This unit is part of the Chemistry library.
Chemistry Layout 6Miriam Calzada
Acids release H+ ions. The Brønsted-Lowry Acid-Base Theory. In reality, H+ ions released from an acid in water combine with water molecules to make hydroxonium ions (H3O+). If HA is any given acid, the ionic equation for forming an acid is: Acids that, like HCl, release only one proton into solution are called monobasic or monoprotic acids.
ACIDS & BASES Past Papers Inside

Acids are species that donate protons; bases are species that accept protons. This is the Bronsted-Lowry definition of acids and bases. In solution, acids 'dissociate' (split apart) and give protons to water molecules, causing hydroxonium ions (H 3 O +) to form. Hydroxonium ions can react with bases, giving the extra proton to the base and.
The Chemistry of Acids and Bases Presentation Chemistry
.PNG)
The Bronsted-Lowry Theory of acids and bases. The theory. An acid is a proton (hydrogen ion) donor. A base is a proton (hydrogen ion) acceptor. The relationship between the Bronsted-Lowry theory and the Arrhenius theory. The Bronsted-Lowry theory doesn't go against the Arrhenius theory in any way - it just adds to it.